Imagine a world where relief from chronic pain could be delivered at the touch of a button, where electrical currents dance through your body to soothe discomfort and promote healing. While this may sound fiction, it’s actually a known technique on how physical therapists use TENS. We’ll be going over the secrecies that this medical device may provide to patients.
Why Do Physical Therapists Use TENS Devices?
TENS devices, or Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation units, have become a staple in many physical therapy practices due to their potential ability to alleviate pain and enhance rehabilitation outcomes.
One of the key benefits of TENS is its dual action: it’s said to provide analgesic effects while promoting blood circulation. This not only helps clients manage chronic pain conditions but also accelerates healing in acute injuries by increasing nutrient delivery to damaged tissues.
Physical therapists often leverage this technology as part of a holistic treatment plan, tailoring the intensity and frequency of electrical impulses to each individual’s needs for optimal efficacy.
Another compelling reason for using TENS in therapy lies in its non-invasive nature. Unlike medications that may come with side effects or invasive procedures that carry risks, TENS offers a drug-free alternative that patients can easily integrate into their daily routines. This is particularly valuable for individuals wary of pharmaceutical interventions or those with contraindications for certain medications.
Common Conditions Treated with TENS
One of the most common conditions treated with TENS therapy is arthritis, where patients often struggle with joint discomfort and stiffness. By sending electrical impulses through the skin, TENS may help to block pain signals from reaching the brain while simultaneously stimulating the production of endorphins, providing natural relief without the need for pharmaceuticals.
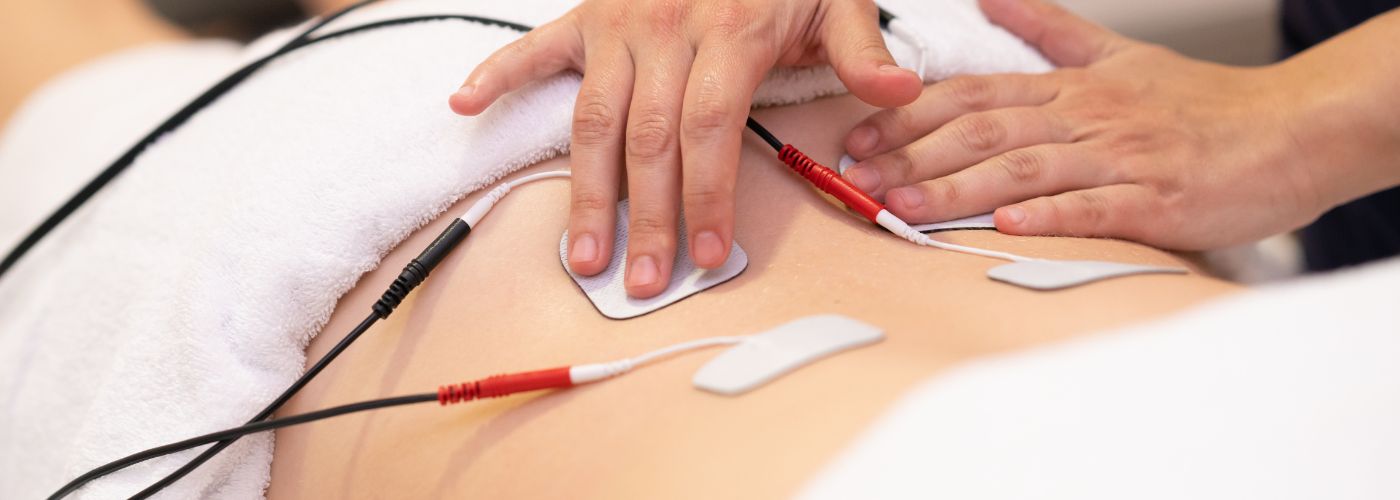
In addition to arthritis, TENS therapy is frequently used for managing lower back pain—a condition that affects millions worldwide. Many people dealing with persistent back issues find that traditional treatments like medication or physical therapy can take time to show effects. TENS provides an immediate approach to alleviating tension and discomfort right at home.
Beyond musculoskeletal pain, TENS has also shown promise in treating headaches and migraines by disrupting their typical pathways and offering a gentle alternative that encourages relaxation through muscle stimulation. Integrating TENS into a holistic treatment plan empowers patients not only to manage their conditions better but also regain control over their wellness journey.
Physical Therapy Techniques Using TENS/EMS
Physical therapists often incorporate TENS & EMS devices into their treatment sessions to enhance pain relief and facilitate muscle recovery. During a typical session, the therapist begins by assessing the patient’s condition, identifying areas of pain or muscle weakness. Once the target areas are determined, electrodes are strategically placed on the skin over these regions.
For TENS therapy, the device delivers low-voltage electrical currents designed to stimulate sensory nerves, which may help block pain signals from reaching the brain while promoting the release of endorphins for natural pain relief.
The therapist adjusts settings such as frequency and intensity based on patient comfort and therapeutic goals. In contrast, EMS is utilized primarily for muscle rehabilitation; it sends electrical impulses that mimic natural muscle contractions, aiding in strengthening weakened muscles or preventing atrophy in immobilized patients.
Throughout the session, therapists closely monitor patient responses to ensure optimal effectiveness and adjust parameters as needed.
Physical Therapy Studies Using TENS Therapy
Emerging research suggests that TENS may play a pivotal role in neuromodulation—improving motor function by affecting the central nervous system’s pathways involved in pain perception and movement control. This has profound implications for conditions such as stroke recovery, where increased neural plasticity can significantly impact rehabilitation progress.
As practitioners begin to integrate this technology into their treatment regimens more frequently, it opens doors for personalized approaches tailored to individual patient needs—transforming standard care protocols into dynamic healing experiences that harness the power of electrical stimulation alongside traditional methodologies.
TENS Safety Measures Used By Physical Therapists
Safety measures are important to ensure patient well-being while maximizing the effectiveness of this treatment. One crucial aspect is thorough patient assessment before initiating TENS therapy. Therapists evaluate medical history, skin sensitivities, and existing conditions that may contraindicate use—such as pacemakers or pregnancy—to tailor the therapy appropriately.
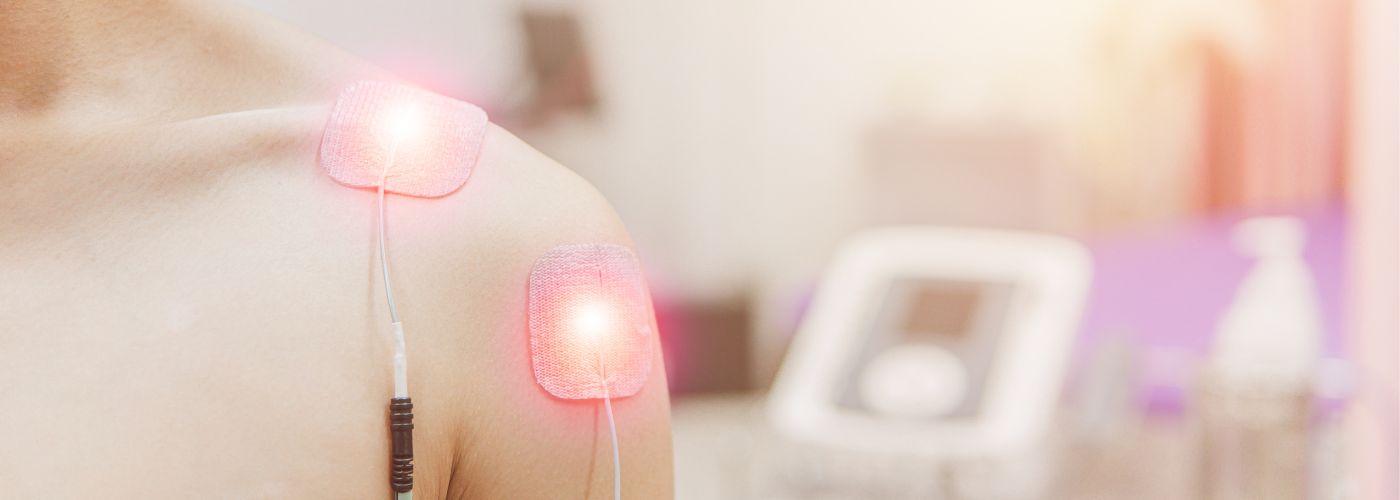
Another vital safety measure involves proper electrode placement and monitoring during TENS application. Physical therapists are trained to select optimal sites based on the patient’s pain pattern, which not only enhances treatment efficacy but also minimizes discomfort.
Regular checks on skin integrity under the electrodes help prevent irritation or burns; this vigilance fosters a safe environment where patients feel cared for and empowered in their recovery journey.
Moreover, practitioners emphasize educating patients about using TENS at home safely post-therapy sessions. By equipping patients with knowledge about duration limits, settings adjustment, and recognizing adverse responses—like excessive discomfort or skin reactions—therapists extend their commitment to safety beyond clinical hours.
Future of TENS & EMS Devices in Physical Therapy
As we look towards the future of TENS and EMS devices in physical therapy, the integration of artificial intelligence and smart technology promises to revolutionize patient care.
Imagine wearable devices that not only deliver targeted electrical impulses but also adjust their settings in real-time based on biofeedback from the patient’s body. This evolution could lead to personalized pain management and rehabilitation plans, optimizing recovery by providing precise stimulation tailored to an individual’s specific needs.
Moreover, the rise of telehealth is reshaping how physical therapy is administered, expanding access for patients regardless of geographical constraints. Future TENS and EMS units may be designed for remote monitoring, allowing therapists to adjust treatment protocols during virtual sessions while ensuring consistent engagement with patients at home.
Related Stories
When Courage Takes Flight: Lessons From a Women’s Skydiving Record Attempt
Photo by Taylor Buffington (T-Buff) We went to Eloy, Arizona on a mission — to...
Nov
Sciatica: 1, LeBron: 0 (For Now)
File photo: LeBron James #6 of the Los Angeles Lakers. (Photo: Thearon W. Henderson /...
Oct
Pickleball vs. Tennis: The Science of Recovery
For years, tennis was the stand-in for movement: endurance, coordination, and power all at once....
Oct
5 Ways to Support Bone Strength with HiDow
World Osteoporosis Day (October 20) October 20 is World Osteoporosis Day, and chances are, you’ve...
Oct
FDA-Cleared Is a Flex. Here’s Why.
Pulling Back the Curtain You’ve seen it on boxes, on websites, in ads: FDA-cleared. It...
Sep
This Is Fibro. This Is Larry.
September is Pain Awareness Month. And we’re not here to give you medical definitions or...
Sep